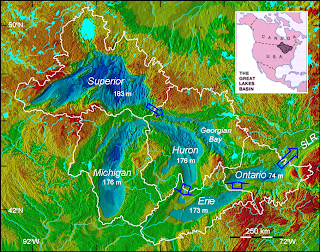
http://www.humble-inc.com/rof_app99-2.htm
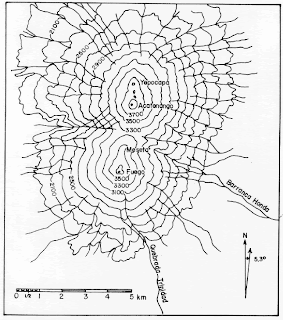
Star Plots compare single data points with different variables. For example, point 1 is larger than 3 but smaller than 2. The figure above is a star plot created from gas chromatographic analysis of oil samples using selected peak ratios.